A suspended floor is a ground floor with a void underneath the structure The floor can be formed in various ways, using timber joists, precast concrete panels, block and beam system or cast insitu with reinforced concrete However, the floor structure is supported by external and internal wallsConcrete Floor Slab Construction Process 1 Assemble and Erect Formwork for Slab;Suspended Timber Ground Floors consist of the finished timber floorboards being attached to floor joists, which are suspended above the subfloor of the foundation These floor joists are raised above the subfloor on small supporting walls called tassel walls (or sleeper walls) A wallplate is then attached to the top of the tassel walls, on

Building Construction I Sofia Sebastian 1 Ppt Download
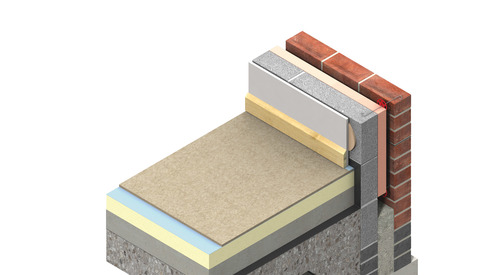
Suspended floor slab detail
Suspended floor slab detail- Also asked, what is a suspended ground floor?E5MCFF30 Suspended InSitu Concrete Floor, Insulation Below Slab Build Up External Masonry Cavity Wall Masonry Outer Leaf (λ = 077) 100mm Aircrete Block Inner Leaf (λ = 019 W/mK) Full Fill Insulation 150mm Cast InSitu Suspended Slab




E5mcpf28 Suspended In Situ Concrete Floor Insulation Below Slab Labc
Composite floor systems In the final state the ribs in the decking serve as void formers in the slab, thereby reducing the weight of floor construction with the knockon benefits this can have It is also possible to suspend services from the soffit of a composite slab, using anchors that are designed to slot into the decking profileVisqueen Radon R400 is a 04mm thick copolymer thermoplastic membrane The product is red in colour and supplied 4m x m in a multifolded roll Complies to BSA11952—Slabsonground, p 2 53—Suspended slabs, p 7 54—Miscellaneous details, p 9 Joseph F Neuber Jr, Chair Patrick J Harrison, Vice Chair Russell E Neudeck, Secretary ACI 3021R15 Guide to Concrete Floor and Slab Construction Reported by Committee 302 Dennis C Ahal Bryan M Birdwell Peter A Craig Allen Face C Rick Felder Edward
4 Curing Concrete and Remove Formwork32—Slabsonground 33—Suspended slabs 34—Miscellaneous details Chapter 4—Site preparation and placing environment, p 3021R17 41—Soilsupport system preparation 42—Suspended slabs 43—Bulkheads 44—Setting screed guides 45—Installation of auxiliary materials 46—Concrete placement conditions Chapter 5—Materials, pConcrete floor systems are reinforced slab structures designed to satisfy a range of loading and span conditions in a building Concrete floor systems are designed to span in either one direction (oneway) or both directions (twoway) of a structural bay
The Suspended Garage Slab Installation Process Coordinating with your architect, engineer, and contractor a composite design is created by a licensed professional engineer for your home After foundation is poured, field measurements are taken to ensure a good fit Steel is detailed, fabricated, and prime painted Steel is erectedBuilding codes re q u i r e that floors and roofs be of fire re s i s t i v e cons t r uction for most occupancies in c e r tain types of buildings There are va r ious ways of providing fire re s i s tance for steel deckre i n f o r ced conc r ete slab systems Details of such c o n s t r uctions are given in publications such as Un d eGround bearing slabs should not be used in ground conditions where heave can occur or where the foundation depth is greater than 15m Under these circumstances a suspended floor construction should be used Site preparation The ground beneath the floor should be stripped of all topsoil, organic matter or tree roots prior to filling and compaction




Suspended Floors All You Need To Know Thermohouse




Concrete Slab Floor Construction Branz Renovate
3 Pour, Compact and Finishing Concrete Floor Slab; For optimum results when addressing heat loss through a suspended timber floor, the specification needs to ensure that high levels of thermal performance delivered by the insulation material are combined with airtightness and moisture control, while at the same time facilitating a degree of breathabilityA selection of floor detail drawings including block and beam floors, timber suspended floors, solid ground floors and upgrade floor details Click the Image for LowRes Preview Cavity Wall Timber Floor £300 vat Add To Basket Includes DWG, DXF and Jpeg Click the Image for LowRes Preview Wall To Floor Detail



Floor Insulation Optimal Insulation




E5smew1 Suspended Beam And Block Floor Insulation Slab Labc
Thickness of the slab is decided based on span to depth ratio specified in IS Minimum reinforcement is 012% for HYSD bars and 015% for mild steel bars The diameter of bar generally used in slabs are 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, 12mm and 16mm Concrete Suspended Slabs Suspended slabs are upper floors of the ground that do not come into direct contact with the Earth They are often used to build floors for the upper stories of the house, but they can also be laid on top of the prebuilt walls to form a floorStudies of the site, carried out in accordance with Chapter 41 'Land quality managing ground conditions' should be taken into account in the design of substructure Where the depth of infill exceeds 600mm, the floor must be designed as a suspended floor, as described in Chapter 52 'Suspended ground floors' (Design) Loadbearing partitions should not be supported off ground bearing floors




Eurima Suspended Concrete Floors



How To Construct A Floating Floor Insulation Kingspan Great Britain
SOLID FLOOR INSULATION OVER SLAB To meet min U value required of 022 W/m²K Solid ground floor to consist of 150mm consolidated wellrammed hardcore Blinded with 50mm sand blinding Provide 100mm ST2 or Gen2 ground bearing slab concrete mix to conform to BS over a 10mm gauge polythene DPM, DPM to be lapped in with DPC in wallsSuspended slabs are made of concrete and steel mesh, the same as a ground slab A suspended floor is a ground floor with a void underneath the structure The floor can be formed in various ways, using timber joists, precast concrete panels, block and beam system or cast insitu with reinforced concrete However, the floor structure is supported by external and internal walls Supports underneath the floor are permanent and include sleeper walls or timber



Construction Details Cype Ehu410 Interior Inverted Beam One Way Floor Slab Ribs Cast In Place



Farm Structures Ch5 Elements Of Construction Floors Roofs
How Does A Suspended Slab Work, In A New Home Construction Suspended reinforced concrete slabs are used in many applications in the construction industry The advantage of a suspended reinforced concrete slab is that it is possible to get highSuspended slabs are aboveground level slabs which are not directly in contact with the earth They are commonly used to create floors for the upper storeys of houses, but can also be sat on top of preconstructed walls to form a ground floor What are suspended slabs made of?Concrete slabs that form the ground floor of a building may be either supported on beams (called a suspended slab) or supported directly on the subsoil, (via hardcore, for example) called a




Suspended Slabs



Floors And Flooring Sans Building Regulations South Africa


